Scaffolding is a temporary structure in the form of a timber or steel framework over which the workmen can sit and carry on the construction work. Scaffolding is needed for new construction, repairs of structure,s or even demolition of a building.
Scaffolding is generally needed when the height of the structural member (wall, column, etc.) is greater than 1.5m. The scaffolding should be made by sufficient strong and stable materials so that it can easily support and carry workman and construction materials placed on it. During construction, as the work progress on upwards, the height of the scaffolding is also increased.
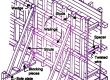
Component parts of scaffolding
Scaffolding has the following components: as shown in Fig. 2.
- Standards: These are the vertical members of the framework, supported on the ground or drums, or embedded into the ground.
- Ledgers: The horizontal supporting members running parallel to the wall.
- Braces: Braces are diagonally fixed on standards.
- Putlogs: Putlogs are placed one end on ledgers and other ends right angles on the wall. This is a transverse member.
- Transoms: Transoms are a type of putlogs supported on ledgers on both sides.
- Bridle: This is a member used to bridge a wall opening; supports one end of the putlog at the opening.
- Boarding: Boarding is a horizontal platform supported on putlogs and is used for the support of workmen and materials at the time working.
- Guard rail: This is a rail, provided like a ledger, at the working level.
- Toeboard: These are boards, placed parallel to ledgers, and supported on putlogs, to give protection at the level of the working platform.

Types of scaffolding
In the construction Process following types of Scaffolding are used:
- Single scaffolding or brick-layers scaffolding.
- Double scaffolding or masons scaffolding.
- Cantilever or needle scaffolding.
- Suspended scaffolding.
- Trestle scaffolding.
- Steel scaffolding.
- Patented scaffolding.
1. Single scaffolding (Brick-layer’s scaffolding)
This consists of a single framework of standards, ledgers, putlogs etc., constructed parallel to the wall at a distance of about 1.20 meters. The standards are placed at 2 to 3 m intervals. At a vertical interval of 1.2 to 1.5 interval ledgers are connected to standards.
Putlogs are placed one end on ledgers and another end right angles on the wall. This is a transverse member,
at an interval of 1.2 to 1.5 m. Guards, boarding and other members are placed as shown in Fig.1. This type of scaffoldings is called putlog scaffolding and is commonly used for bricklaying.
2. Double or mason’s scaffolding
In stone masonry, it is very difficult to provide holes m the wall to support putlogs. In that case, two rows of scaffolding are used more strongly.
Each row thus forms a separate vertical framework. The first row and second row are placed at 20 to 30 cm and 1.2 to 1.5 m away from the wall respectively. Putlogs are then supported on both the frames. Rakers and cross braces are connected with this to make more strong and stable. Such scaffolding is also called ‘independent scaffolding.
3. Cantilever or needle
Cantilever or needle is used under the following circumstances:
(i) Ground is weak to support standards.
(ii) When the upper part of the wall is to be carried out.
(iii) It is required to keep the space, near the wall, free for a walk and for traffic, etc.
The scaffolding may be a single type (putlog scaffolding), as shown in fig.3. or double type (independent scaffolding), as shown in Fig.4.
In the former type, needles are projected from Opening or through holes in the wall to support the standards. In the second type, the needles are strutted inside the floors by making an opening.
4. Suspended scaffolding
This type of scaffolding is normally used for repair works such as pointing, painting, etc., wire ropes or chains are connected to the working platform of the scaffolding and is suspended from the roof of the building. And by using rope or chain, the platform can be raised or lowered at any required level. It is a lightweight scaffolding.
5. Trestle scaffolding
This type of scaffolding is used for painting and repair works inside the room, less than a height of 5 m. The working platform is supported on the top of movable contrivances such as tripods, ladders, etc. mounted on wheels.
6. Steel scaffolding
In steel scaffolding instead of using wooden members, steel tubes are used and steel couplets or fittings are used instead of rope lashings, other things are similar to the wooden types.
Such scaffolding can be erected and dismantled rapidly. Steel scaffolding is now days using is high rise building because of its greater strength, greater durability, and higher fire resistance. Through its initial cost is more but its salvage value is higher. It is extensively used these days. Fig shows steel scaffolding both for the brick wall as well as a stone wall.
7 . Patented scaffolding
Normally in the market patented scaffolding, made of steel is available. These scaffoldings are an arrangement with special couplings, frames, etc. the working platform is supported on brackets which can be adjusted at any suitable height.